Track mileage automatically
Get startedCents Per KM Tax Deduction
The cents per km tax deduction term refers to the process of claiming business-related car expenses based on the cents per km rate from the ATO. You can claim a cents per km deduction each year on your tax return.
Who can claim a cents per km deduction
As an employee, a sole trader, in a partnership, or as a business owner, you might be eligible to claim a cents per km tax deduction.
- Employees can claim cents per km deductions if they are not reimbursed by their employer for business-related driving.
- Sole traders and partnerships (where at least one party is an individual) can claim cents per km tax deductions
Regardless of your employment situation, you can only use the cents per km method to claim tax deductions for cars. Cars are defined by the ATO as motor vehicles that can carry no more than a tonne of load and no more than 9 passengers. Note that motorcycles are not considered cars for the purpose of ATO tax deductions.
If you use another type of vehicle for business purposes, have a different employment situation, or want to claim more than 5000 kilometres a year you can claim km tax deductions through other methods.
Learn more about how to claim deductions for business driving in our
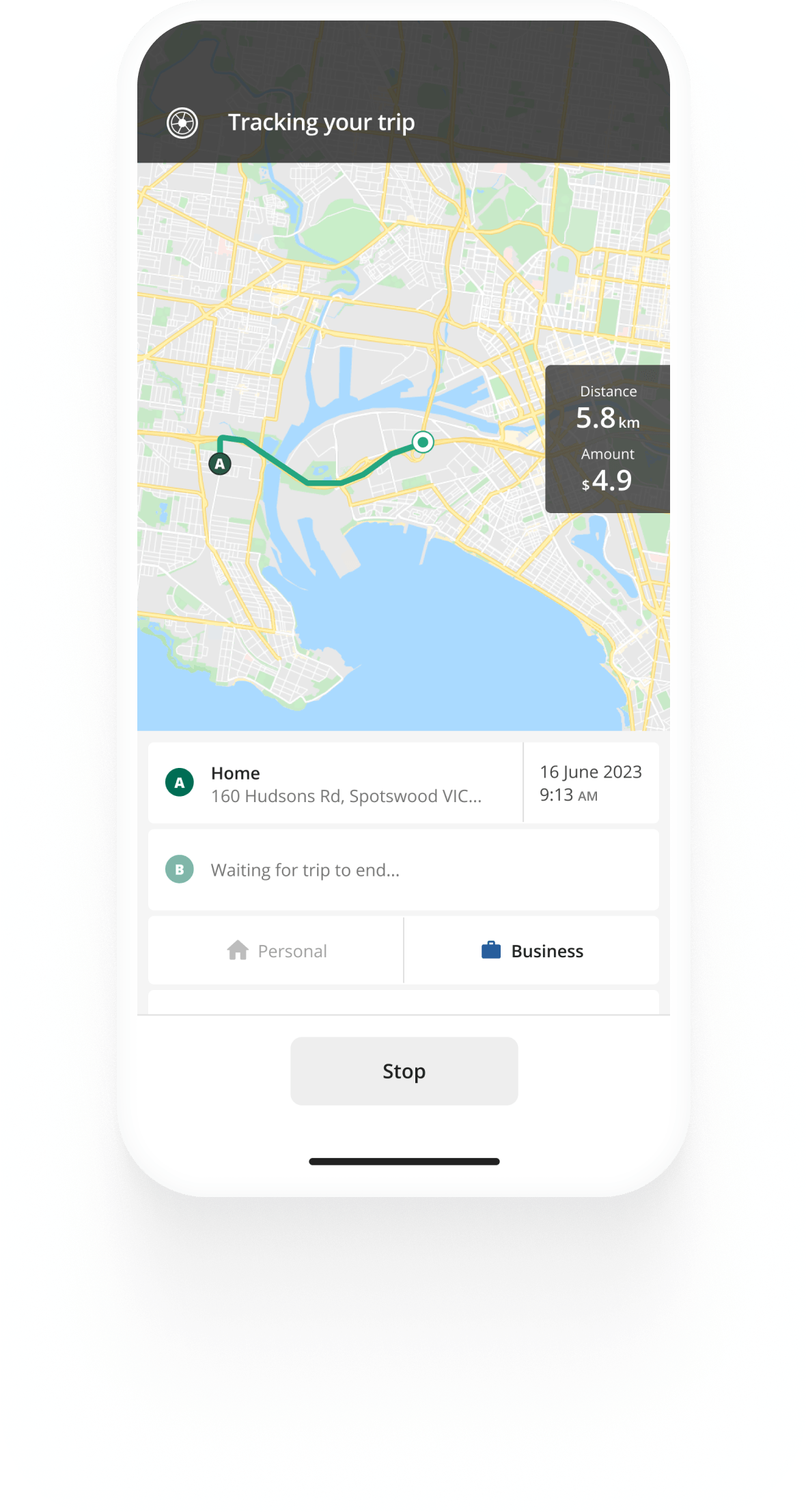

Kilometre tracking made easy
Trusted by millions of drivers
Automate your logbook Automate your logbook
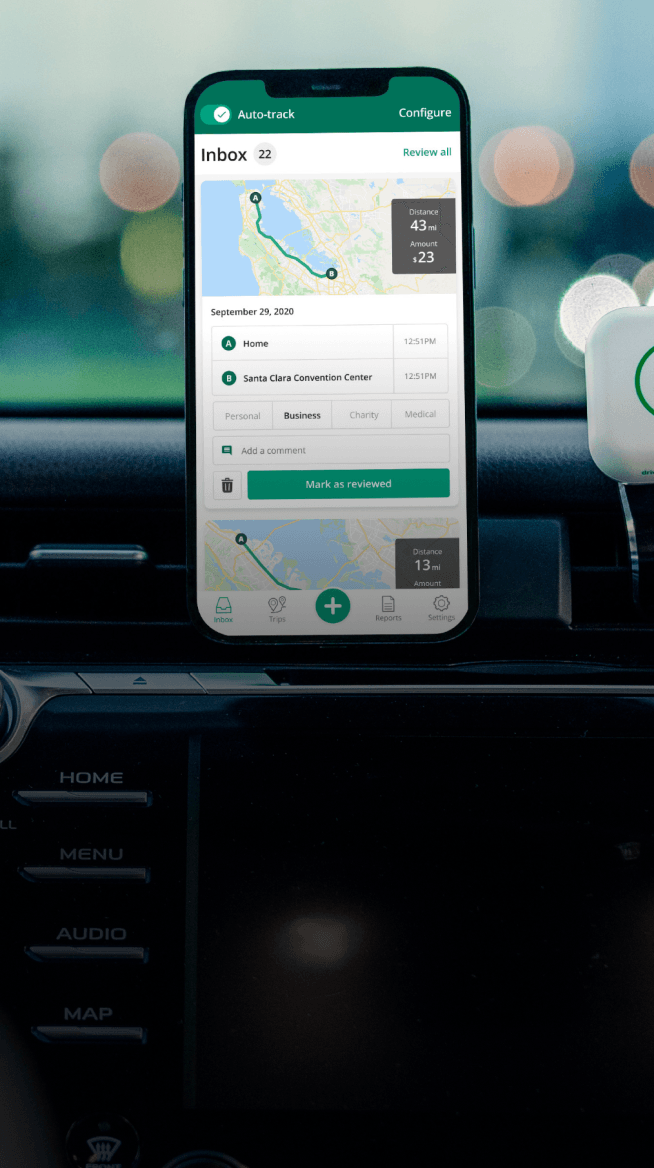
Automatic mileage tracking and ATO-compliant reporting.
Get started for free Get started for freeHow does the cents per km tax deduction work?
The Australian Tax Office publishes an update cents per km rate each year. The rate is meant to cover all expenses of running your car for business-related purposes. Use the cents per km rate to calculate the tax deduction you can claim for the year. You can do so by multiplying your business-related kilometres with the corresponding year’s rate.
When you claim your cents per km tax deduction, you don’t need to provide evidence of how many kilometres you’ve driven. However, this doesn’t mind you don’t need to keep records. The ATO may ask you to see how you’ve calculated your claim or you might be audited. You should still record information about each trip with the following details:
- The number of kilometres driven for business and personal purposes.
- Details of how you calculated your claim.
If you use another tax deduction method, you might have to keep additional records.
Learn more about claiming cents per km tax deductions and other methods in our ATO guide.
FAQ
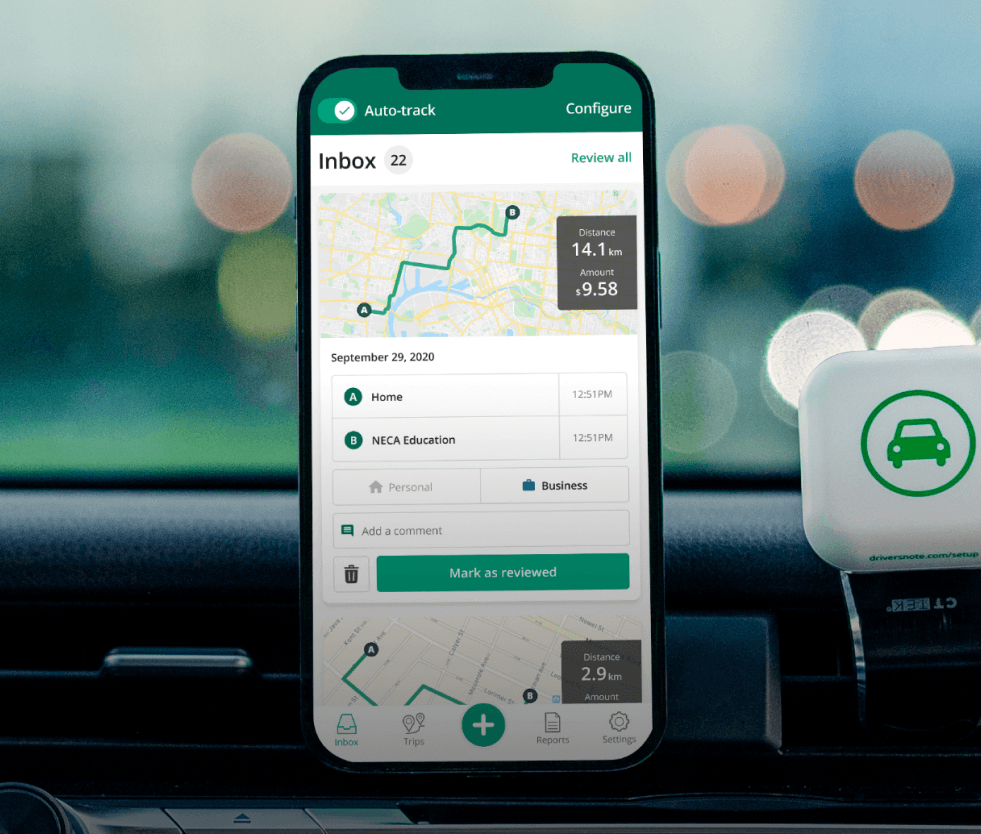
Tired of logging mileage by hand?
Effortless. ATO-compliant. Liberating.
Related posts
ATO Mileage Guide
25 June 2024 - 5 min read
Learn about the rules of reimbursing employees for their car expenses or deducting expenses as an employee or self-employed individual.
Employers' Guide to FBT-Exempt Benefits
14 April 2025 - 2 min read
Find out how to reduce the amount of FBT you owe by providing various FBT-exempt benefits to your employees.
How to Write Off a Car for Business in Australia
24 February 2025 - 2 min read
Don't miss out on writing off a car for business - it may be the largest deduction you can claim as a business owner. See the 2024/25 ATO rules.

.svg)
.svg)