Track mileage automatically
Get startedFBT (Fringe Benefit Tax)
FBT, or Fringe Benefits Tax, is a tax that is imposed on employers in Australia for providing certain benefits to their employees, including the use of a company car or a take-home vehicle. FBT is designed to ensure that employers are not able to avoid their tax obligations by providing non-cash benefits to their employees instead of cash payments.
FBT is a separate tax from income tax and is paid by the employer, not the employee. The rate of FBT is currently set at 47%, which is the top marginal tax rate in Australia. This means that for every dollar of fringe benefits provided to an employee, the employer must pay an additional 47 cents in tax.
Common examples of fringe benefits that are subject to FBT
The types of benefits that are subject to FBT in Australia include the use of a company car or take-home vehicle, private health insurance, entertainment expenses, and more.
Company cars
Track and share your business kilometres with your employer at the touch of a button. Try the automated Driversnote logbook app for free.
If an employee is provided with a car for both work-related and personal use, the employer may be required to pay FBT on the value of the benefit provided. The FBT payable will depend on the type of car, its value, and how much it is used for personal purposes.
The use of a company car or take-home vehicle is one of the most common fringe benefits that are subject to FBT in Australia. When an employer provides an employee with a company car or take-home vehicle, the employee is considered to be receiving a non-cash benefit. This means that the employer is required to pay FBT on the value of the benefit provided. The value of the benefit is determined by the cost of the car or vehicle, as well as any associated expenses, such as fuel, maintenance, and insurance.
See how to keep compliant ATO logbook records of your driving.
Health insurance
If an employer provides health insurance for their employees, the value of the benefit provided may be subject to FBT.
Entertainment expenses
If an employer provides entertainment to their employees, such as tickets to a concert or sporting event, the value of the benefit provided may be subject to FBT.
Employee discounts
If an employee receives a discount on products or services provided by their employer, the value of the benefit may be subject to FBT.
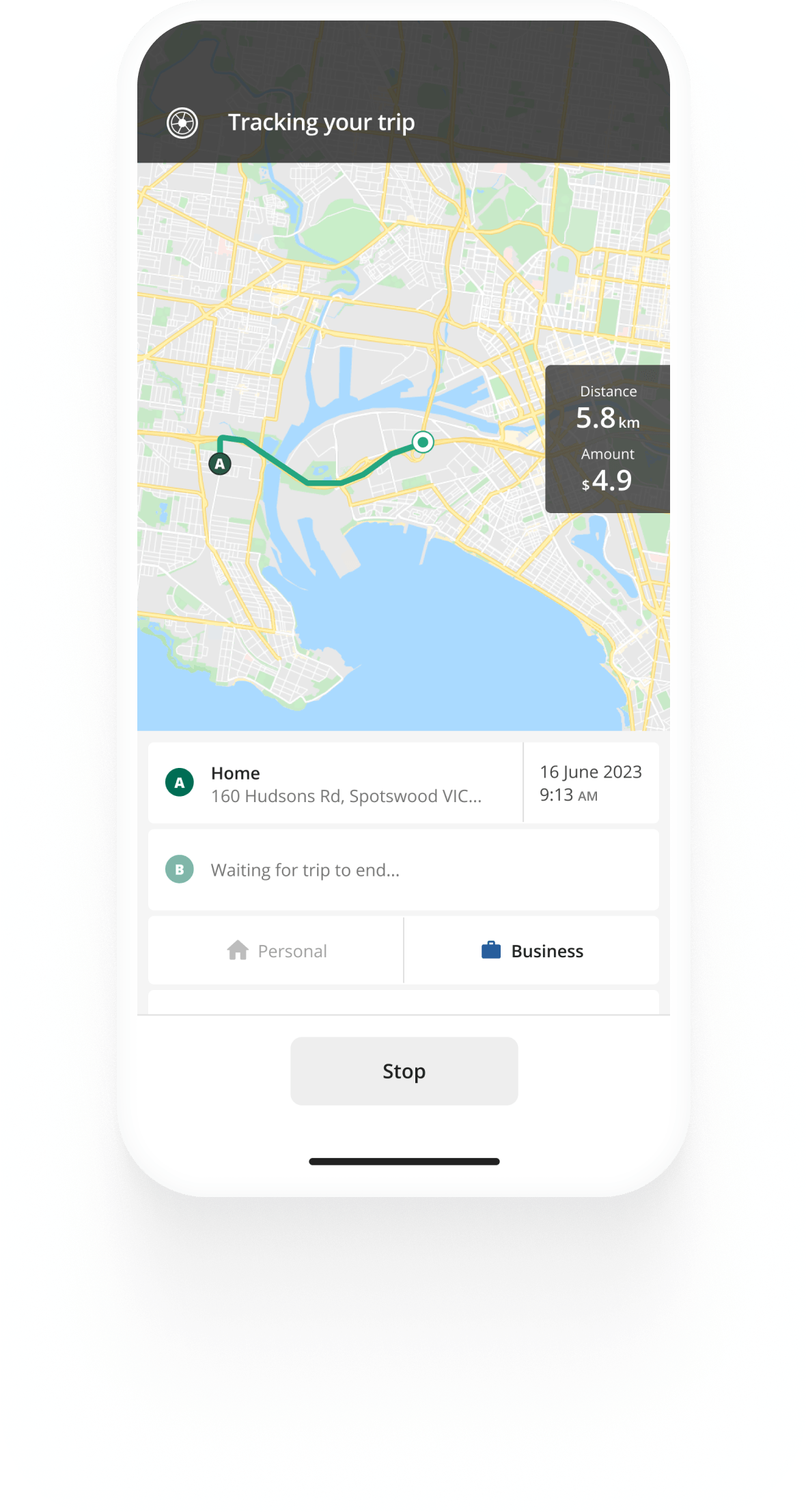

Kilometre tracking made easy
Trusted by millions of drivers
Automate your logbook Automate your logbook
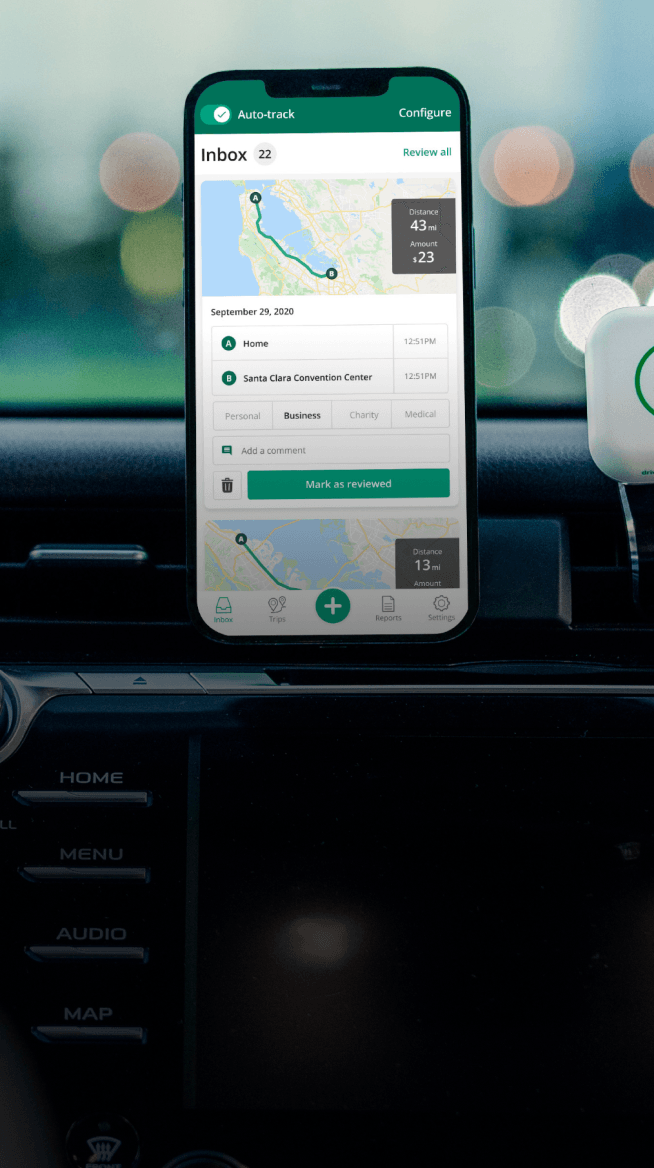
Automatic mileage tracking and ATO-compliant reporting.
Get started for free Get started for freeFBT exemptions
It's important to note that not all fringe benefits are not taxed with FBT. Certain benefits, such as work-related expenses and certain types of insurance, are exempt from FBT.
These benefits include work-related items such as laptops, mobile phones, and tools, as well as certain types of work-related training and education. Other exemptions include certain types of health-related benefits, such as flu vaccinations and health checks, and certain types of entertainment benefits, such as Christmas parties and other social events.
Note that the rules around FBT car exemptions can be complex, and employers should seek professional advice to ensure they are meeting their obligations and avoiding any potential penalties or fines.
FAQ
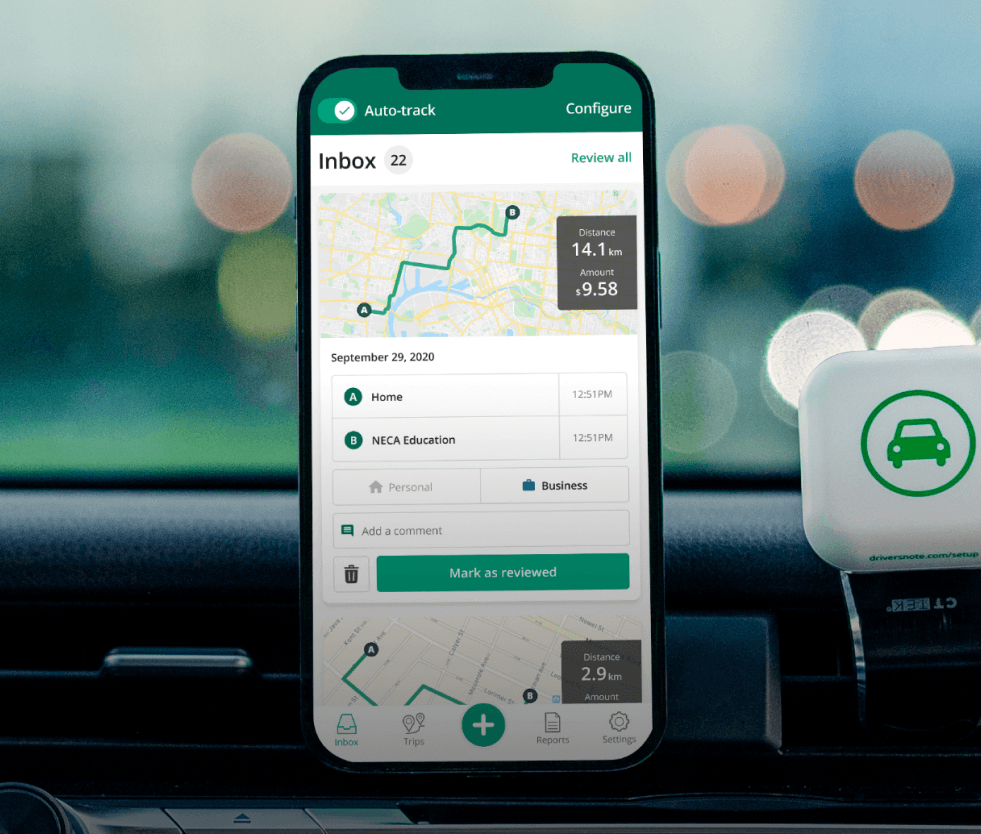
Tired of logging mileage by hand?
Effortless. ATO-compliant. Liberating.
Related posts
ATO Mileage Guide
25 June 2024 - 5 min read
Learn about the rules of reimbursing employees for their car expenses or deducting expenses as an employee or self-employed individual.
Employers' Guide to FBT-Exempt Benefits
14 April 2025 - 2 min read
Find out how to reduce the amount of FBT you owe by providing various FBT-exempt benefits to your employees.
How to Write Off a Car for Business in Australia
24 February 2025 - 2 min read
Don't miss out on writing off a car for business - it may be the largest deduction you can claim as a business owner. See the 2024/25 ATO rules.

.svg)
.svg)