Track mileage automatically
Get startedTax Liability
In this article
Tax liability refers to the amount of tax a taxpayer owes to a tax authority based on their taxable income and the tax rates applicable to their income bracket. It is the legal responsibility of individuals, businesses, and other taxable entities to pay taxes on their income, profits, capital gains, or any other taxable transactions.
What is tax liability?
Tax liability is determined by calculating the taxable income, which is the total income earned minus any allowable deductions and exemptions. The tax liability is then calculated based on the tax rates set by the tax authorities.
Tax liability can vary depending on the tax laws and regulations of different countries or jurisdictions. Additionally, tax liability can be influenced by various factors such as filing status, eligible deductions, and tax credits.
Your tax liability doesn't just account for the current year; it also factors in previous years for which you might owe taxes.
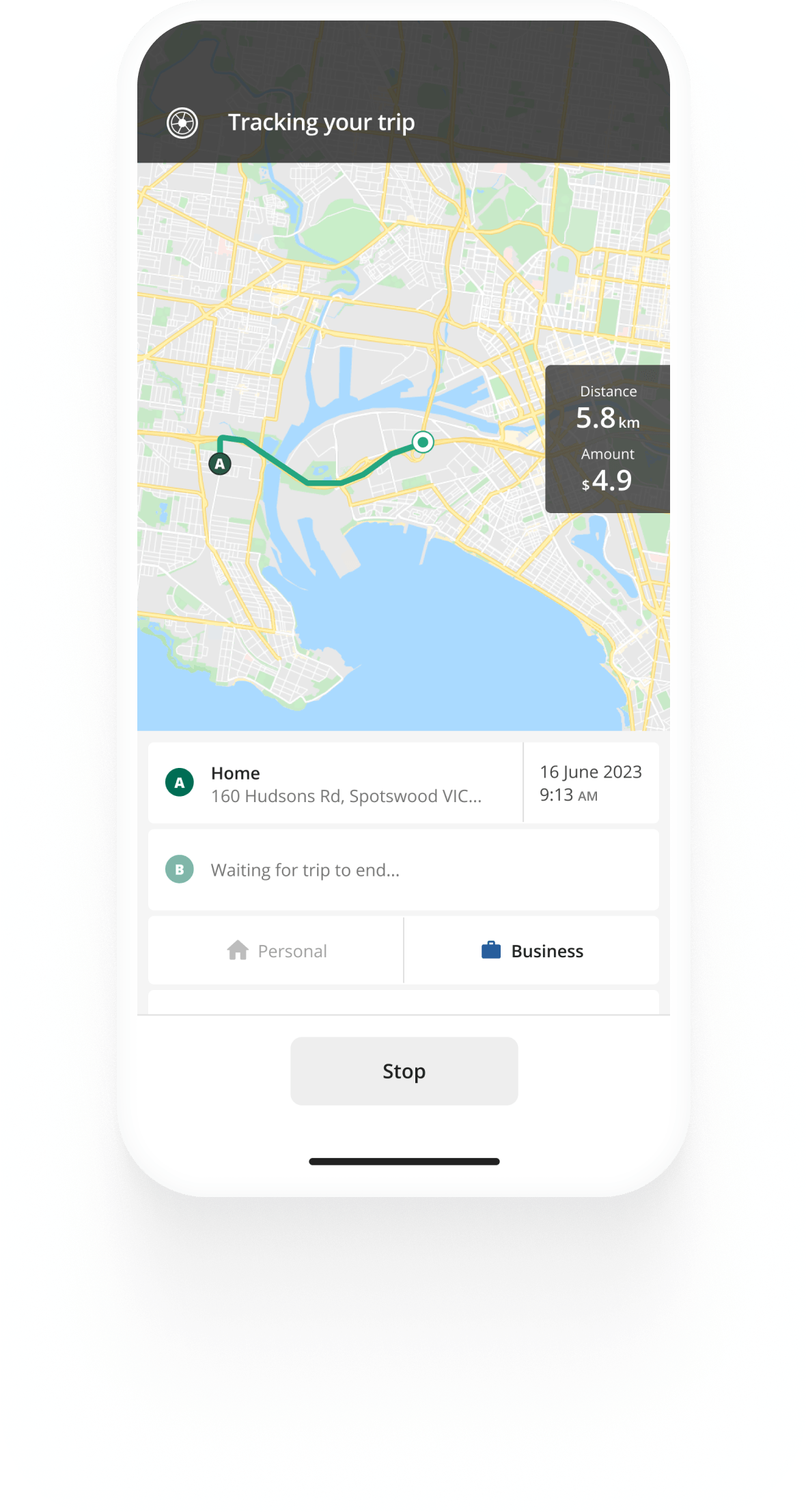

Kilometre tracking made easy
Trusted by millions of drivers
Automate your logbook Automate your logbook
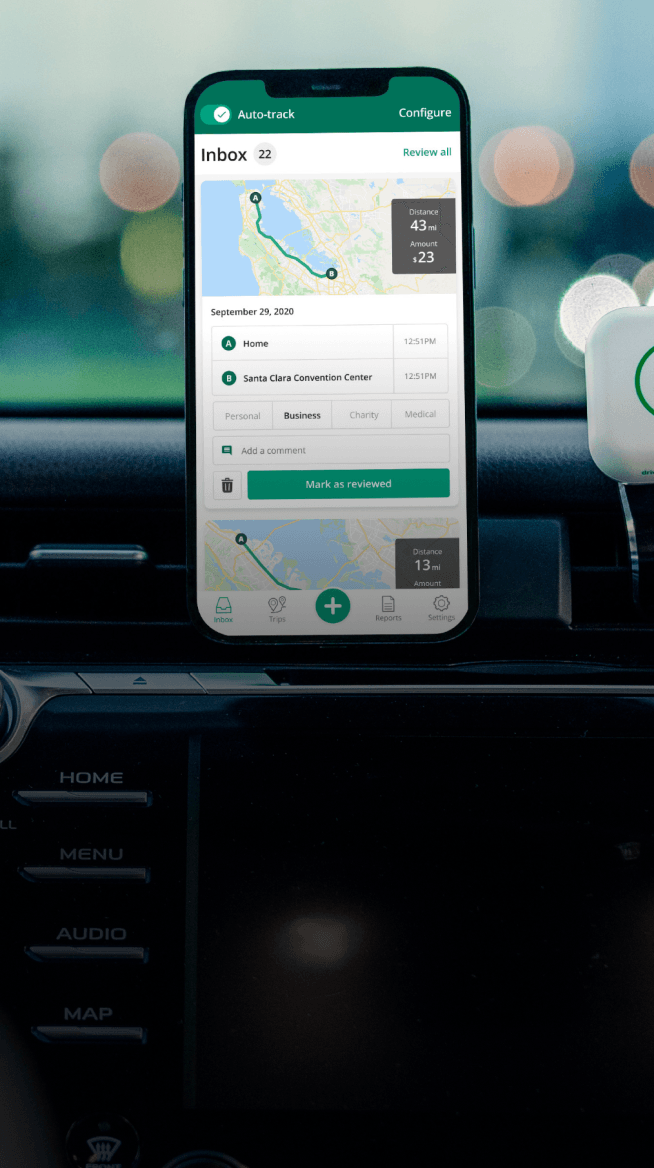
Automatic mileage tracking and ATO-compliant reporting.
Get started for free Get started for freeWhat affects tax liability
Several factors influence the calculation of tax liability. The most common ones include:
Income
For individuals, the primary source of tax liability is their income. This includes wages, salaries, tips, and other forms of earnings. In most countries, income tax rates vary depending on the amount earned. Generally, higher incomes are subject to higher tax rates.
Business profits
Tax liability for businesses is based on their net profits after deducting allowable business expenses from their total revenue. Corporate tax rates often differ from individual tax rates.
Capital gains
Tax liability can also arise from the sale of assets like stocks, real estate, or other investments. The difference between the purchase price and the selling price is considered a capital gain and may be subject to taxes.
Deductions and credits
Tax deductions and credits can help reduce tax liability. Deductions, such as those for mortgage interest or charitable donations, reduce taxable income. Credits, on the other hand, directly reduce the amount of tax owed.
Filing status
Tax liability can vary based on individuals’ filing status (e.g., single, married, head of household). Different statuses have different tax brackets and deductions.
Determining tax liability
To determine tax liability accurately, individuals and businesses are required to file tax returns with the government authorities. Taxpayers must report their income, deductions, and any applicable credits on the tax return form. The tax return will calculate the total tax liability, and if the taxpayer has already paid some taxes throughout the year (e.g., through employer withholding), the amount already paid will be deducted to arrive at the final amount owed or refunded.
FAQ
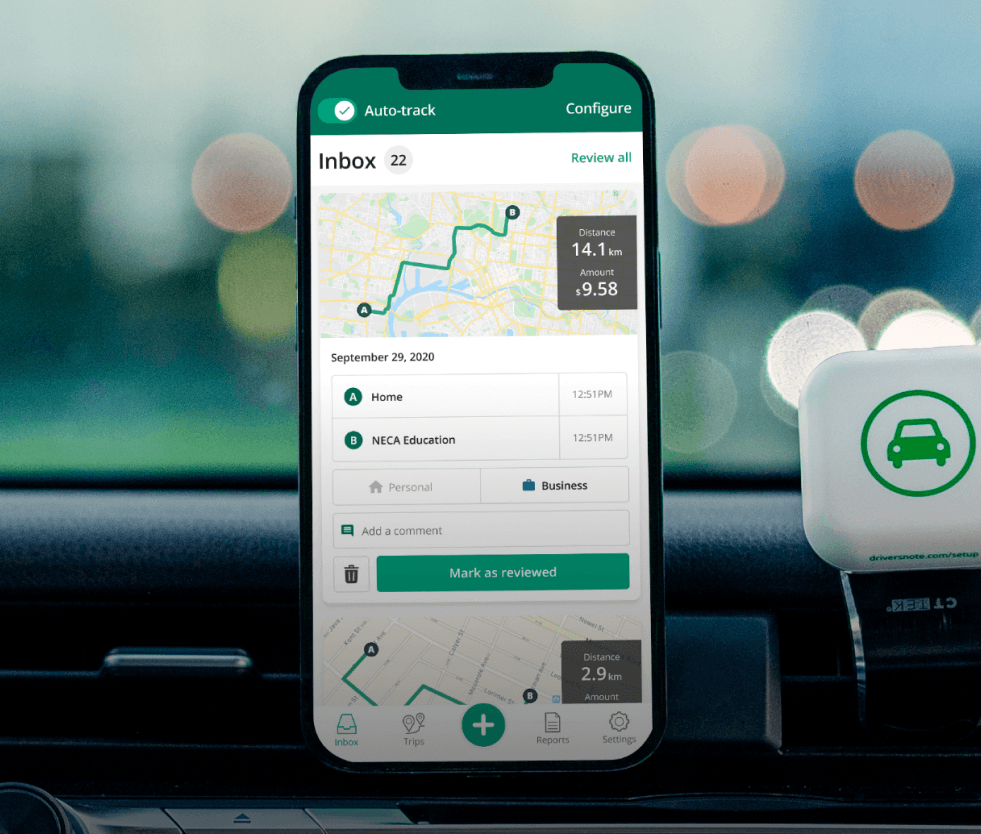
Tired of logging mileage by hand?
Effortless. ATO-compliant. Liberating.
Related posts
ATO Mileage Guide
25 June 2024 - 5 min read
Learn about the rules of reimbursing employees for their car expenses or deducting expenses as an employee or self-employed individual.
Employers' Guide to FBT-Exempt Benefits
14 April 2025 - 2 min read
Find out how to reduce the amount of FBT you owe by providing various FBT-exempt benefits to your employees.
How to Write Off a Car for Business in Australia
24 February 2025 - 2 min read
Don't miss out on writing off a car for business - it may be the largest deduction you can claim as a business owner. See the 2024/25 ATO rules.

.svg)
.svg)